Page 1601 - MISUMI Thailand Economy Series
P. 1601
[Technical Data] [Technical Data]
Selection of Ball Screws 4 Selection of Conveyor Timing Belts
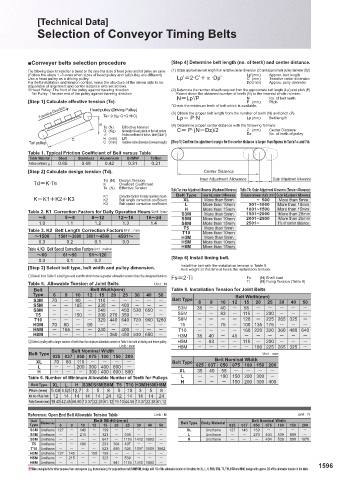
①Constant Speed Torque Exerted on the Motor Output Thread ■Conveyer belts selection procedure [Step 4] Determine belt length (no. of teeth) and center distance.
This is the amount of torque required to drive the output thread against the applied external load, at a constant speed.
The following steps for selection is based on the case that sizes of head pulley and tail pulley are same. (1) Obtain approximate belt length from tentative center dimension (C') and approximate pulley diameter (Dp').
(Follow the steps 1 -3 even when sizes of head pulley and tail pulley are different) Lp' (mm) Approx. belt length
Use a head pulley as a driving pulley. Lp’=2·C’+Q·Dp’ C' (mm) Tentative center dimension
For belt installation and tension control, make the structure of the driven side to be Dp'(mm) Approx. pully diameter
adjustable of alignment and center distance with set screws.
※ Head Pulley: The front of the pulley against traveling direction (2) Determine the number of teeth required from the approximate belt length (Lp') and pitch (P).
Tail Pulley: The rear end of the pulley against traveling direction Round down the obtained number of teeth (N) to the nearest whole number.
[Step 1] Calculate effective tension (Te). N=Lp’/P N No. of belt teeth
P (mm)
Pitch
*Check the minimum teeth of belt which is available.
Traveling Direction Head pulley (Driving Pulley) (3) Obtain the proper belt length from the number of teeth (N) and pitch (P).
Te= 9.8(μ·G+G·H/C)
Lp= P·N
Belt length
Lp (mm)
H Te (N) Effective tension (4) Determine proper center distance with the following formula:
G (Kg) Net weight of load placed on the belt surface C= P·(N-Dz)/2 C (mm) Center Distance
O Friction coefficient of belt vs. table (Table 1) Dz No. of teeth of pulley
C H (mm) Lift
Tail pulley C (mm) Tentative center dimension (conveyor length) [Step 5] Confirm the ajustment margin for the center distance is larger than figures in Table7-a and 7-b.
Table 1. Typical Friction Coefficient of Belt versus Table
Table Material Steel Stainless Aluminium UHMW Teflon
Friction coefficient: O 0.65 0.68 0.42 0.31 0.21
[Step 2] Calculate design tension (Td). Center Distance
②Acceleration Torque Exerted on the Motor Output Thread Td (N) Design Tension Inner Adjustment Allowance Outer Adjustment Allowance
This is the amount of torque required to drive the output shaft against the external load during acceleration. Td=K·Te K Overload Coefficient
Te (N) Effective Tension Table 7-a: Inner Adjustment Allowance (Attachment Allowance) Table 7-b: Outer Adjustment Allowance (Tension Allowance)
K=K1+K2+K3 K1 Correction factors for daily operation hours Belt Type Inner Adjustment Allowance Distance between shafts (mm) Outer Adjustment Allowance
More than 5mm
~ 500
XL
More than 5mm
K2
Belt length correction coefficient
K3 Belt speed correction coefficient L More than 10mm 501~1000 More than 10mm
H More than 15mm 1001~1500 More than 15mm
Table 2. K1 Correction Factors for Daily Operation Hours Unit: hour S3M More than 5mm 1501~2000 More than 20mm
~5 5~8 8~12 12~16 16~24 S5M More than 10mm 2001~2500 More than 25mm
1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 S8M More than 15mm 2501~ 1% of center distance
T5
More than 5mm
Table 3. K2 Belt Length Correction Factors Unit : mm T10 More than 10mm
~1500 1501~3000 3001~4500 4501~ H3M More than 5mm
0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 H5M More than 10mm
Table 4. K3 Belt Speed Correction Factors Unit : m/min H8M More than 15mm
~60 61~90 91~120 [Step 6] Install timing belt.
0.0 0.1 0.2
[Step 3] Select belt type, belt width and pulley dimension. Install the belt with the installation tension in Table 8.
Axis weight at this time is twice the installation tension.
①Select from Table 5 a belt type and a width which have a greater allowable tension than the designed tension. Fs=2·Ti Fs (N) Shaft load
Table 5. Allowable Tension of Joint Belts Unit : N Ti (N) Fixing Tension (Table 8)
Belt Belt Width(mm) Table 8. Installation Tension for Joint Belts
Type 6 9 10 12 15 20 25 30 40 50 Belt Width(mm)
S3M 70 - 80 - 110 - - - - - Belt Type 6 9 10 12 15 20 25 30 40 50
S5M - - 165 - 230 - 400 - - -
S8M - - - - 240 - 450 530 650 - S3M 35 - 40 - 55 - - - - -
T5 - - 150 - 200 270 350 - - - S5M - - 83 - 115 - 200 - - -
T10 - - - - 320 440 640 720 960 1280 S8M - - - - 120 - 225 265 325 -
H3M 70 80 - 90 - - - - - - T5 - - 75 - 100 135 175 - - -
H5M - 165 - - 230 - 400 - - - T10 - - - - 160 220 320 360 480 640
H8M - - - - - 360 450 530 650 - H3M 35 40 - 45 - - - - - -
②Select a pulley with a larger number of teeth than the minimum allowable number in Table 6 for both of driving and driven pulley. H5M - 83 - - 115 - 200 - - -
③Total Torque Exerted on the Motor Output Thread Unit : mm H8M - - - - - 180 225 265 325 -
Belt Nominal Width
Overall torque can be obtained by adding results from formulas ①and②. Belt Type 025 037 050 075 100 150 200 Unit : mm
PL (3PL-P) Z1 2 QN XL 70 80 110 - - - - Belt Type Belt Nominal Width
TM=T1+T2= +TP +JM ×10 (N·cm) 025 037 050 075 100 150 200
-3
2Q˝ 3PL Z2 60t L - - 200 300 400 600 -
H - - - 300 400 600 800 XL 35 40 55 - - - -
Table 6. Number of Minimum Allowable Number of Teeth for Pulleys L - - 100 150 200 300 -
Belt Type XL L H S3M S5M S8M T5 T10 H3M H5M H8M H - - - 150 200 300 400
Pitch (mm) 5.08 9.525 12.7 3 5 8 5 10 3 5 8
Min. No. of Pully Teeth 12 14 14 14 14 24 12 14 14 14 24
Pully Diameter (mm) 19.40 42.45 56.60 13.37 22.28 61.12 19.10 44.56 13.37 22.28 61.12
Once you have temporarily found the type of motor you need, check
1.effective torque, Reference: Open End Belt Allowable Tension Table Unit : N Unit : N
Belt
2.acceleration constant and Type Material 6 9 10 12 Belt Width(mm) 25 30 40 50 Belt Type Body Material 025 037 Belt Nominal Width 150 200
050
075
20
15
100
3. motor overload properties and heat tolerance during repeated S3M Urethane 127 - 145 - 159 - - - - - XL Urethane 127 145 159 - - - -
S5M Urethane - - 215 - 323 - 539 - - - L Urethane - - 270 404 539 809 -
starting, stopping. It is necessary to ensure a sufficient margin for S8M Urethane - - - - 647 - 1176 1412 1882 - H Urethane - - - 404 539 809 1078
these parameters. T5 Urethane - - 196 - 291 394 497 - - -
T10 Urethane - - - - 523 695 926 1097 1509 1862
H3M Urethane 127 145 - 150 159 - - - - -
H5M Urethane - 215 - - 323 - 539 - - -
1595 H8M Urethane - - - - - 941 1176 1412 1882 - 1596
When using belts for other purpose than conveyance (e.g. transmission), for polyurethane belt S3M/H3M; design with 1/2 of the allowable tension in the table; for XL, L, H, S5M, S8M, T5, T10, H5M and H8M, design with approx. 2/3 of the allowable tension in the table.
KJTIV JOEC
KJTIV JOEC